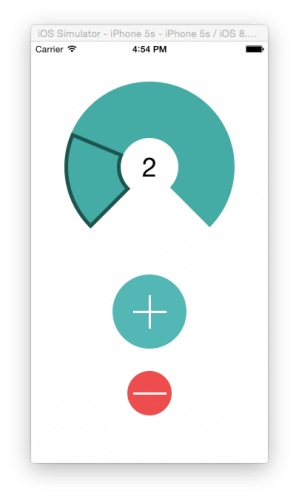
Imagine you’ve finished your app and it works just fine, but the interface lacks style. You could draw several sizes of all your custom control images in Photoshop and hope that Apple doesn’t come out with a @4x retina screen… or, you could think ahead and use Core Graphics to create one image in code that scales crisply for any device size.
Core Graphics is Apple’s vector drawing framework – it’s a big, powerful API and there’s a lot to learn. But never fear – this three-part series will ease you into it by starting out simple, and by the end you’ll be able to create stunning graphics ready to use in your apps.
This is a brand new series, with a modern approach to teaching Core Graphics. The series also covers cool features like @IBDesignable and @IBInspectable that make learning Core Graphics fun and easy.
So grab your favorite beverage, it’s time to begin!
Introducing Flo – One glass at a time
You’ll be creating a complete app to track your drinking habits.
Specifically, it makes it easy to track how much water you drink. “They” tell us that drinking eight glasses of water a day is healthy, but it’s easy to lose track after a few glasses. This is where Flo comes in; every time you polish off a refreshing glass of water, tap the counter. You’ll also see a graph of your previous seven days’ consumption.
In the first part of this series, you’ll create three controls using UIKit’s drawing methods.
Then in part two, you’ll have a deeper look at Core Graphics contexts and draw the graph.
In part three, you’ll create a patterned background and award yourself a homemade Core Graphics medal. :]
Getting Started
Your first task is to create your very own Flo app. There is no download to get you going, because you’ll learn more if you build it from the ground up.
Create a new project (File\New\Project…), select the template iOS\Application\Single View App and click Next.
Fill out the project options. Set the Product Name to Flo, the Language to Swift, and click Next.

On the final screen, uncheck Create Git repository and click Create.
You now have a starter project with a storyboard and a view controller.
Custom Drawing on Views
There are three steps for custom drawings:
- Create a
UIViewsubclass. - Override
draw(_:)and add some Core Graphics drawing code. - There is no step 3 – that’s it! :]
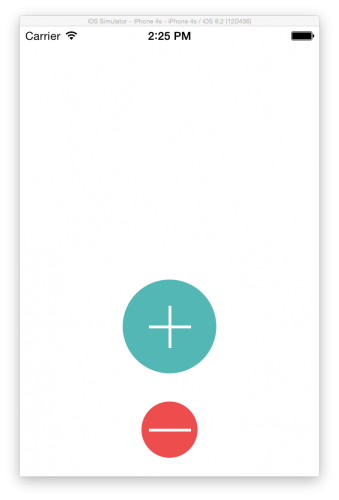
You’ll try this out by making a custom-drawn plus button, like this:
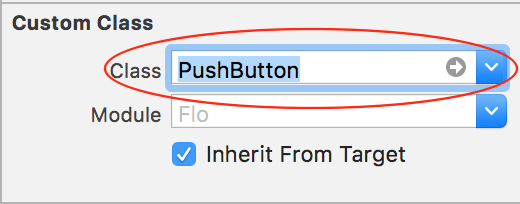
Create a new file (File\New\File…), choose iOS\Source\Cocoa Touch Class, click Next. In this screen, name the new class PushButton, make it a subclass of UIButton, and ensure the language is Swift. Click Next and then Create.
UIButton is a subclass of UIView, so all methods in UIView, such as draw(_:), are also available in UIButton.
In Main.storyboard, drag a UIButton into the view controller’s view, and select the button in the Document Outline.
In the Identity Inspector, change the class to use your own PushButton.
Auto Layout Constraints
Now you’ll set up the Auto Layout constraints (text instructions follow):
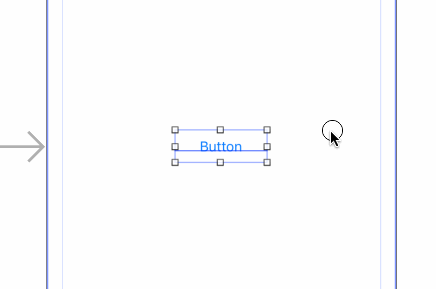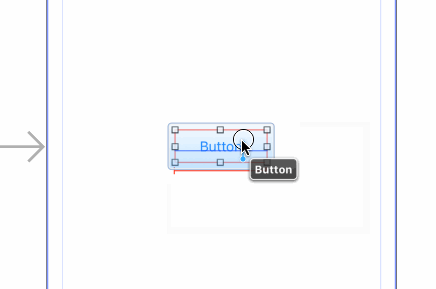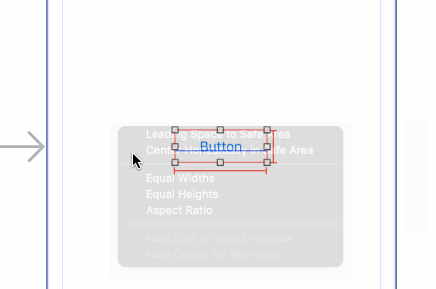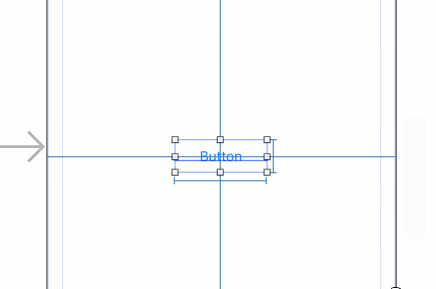
- With the button selected, Control-drag from the center of the button slightly left (still within the button), and choose Width from the popup menu.
- Similarly, with the button selected, control-drag from the center of the button slightly up (still within the button), and choose Height from the popup menu.
- Control-drag left from inside the button to outside the button, and choose Center Vertically in Safe Area.
- Finally control-drag up from inside the button to outside the button and choose Center Horizontally in Safe Area.
This will create the four required Auto Layout constraints; you can now see them in the Size Inspector:
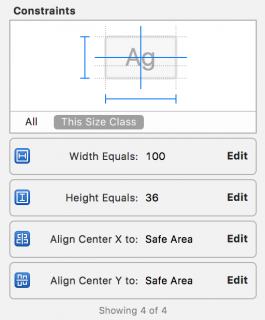
Click Edit on the Align center Y constraint, and set its constant to be 100. This will shift the vertical position of the button from the center to 100 points below the center. Change the Width and Height constraint constants to be equal to 100 too. The final constraints should look like this:
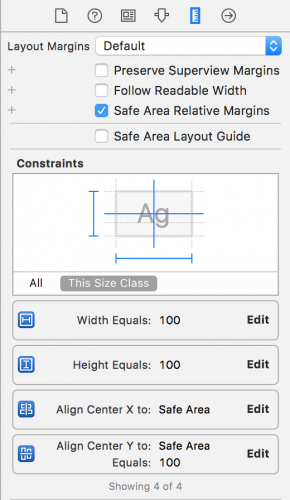
In the Attributes Inspector, remove the default title “Button”.
You can build and run at this point if you’d like, but right now you’ll just see a blank screen. It’s time to fix that up!
Drawing the Button
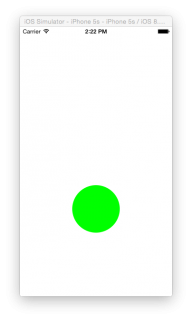
Recall the button you’re trying to make is circular:
To draw a shape in Core Graphics, you define a path that tells Core Graphics the line to trace (like two straight lines for the plus) or the line to fill (like the circle which should be filled here). If you’re familiar with Illustrator or the vector shapes in Photoshop, then you’ll easily understand paths.
There are three fundamentals to know about paths:
- A path can be stroked and filled.
- A stroke outlines the path in the current stroke color.
- A fill will fill up a closed path with the current fill color.
One easy way to create a Core Graphics path is through a handy class called UIBezierPath. This lets you easily create paths with a user-friendly API, whether you want to create paths based on lines, curves, rectangles, or a series of connected points.
Try using UIBezierPath to create a path, and then fill it with a green color. To do this, open PushButton.swift and add this method:
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
let path = UIBezierPath(ovalIn: rect)
UIColor.green.setFill()
path.fill()
}
First, you create an oval-shaped UIBezierPath that is the size of the rectangle passed to it. In this case, it’ll be the size of the 100×100 button you defined in the storyboard, so the “oval” will actually be a circle.
Paths themselves don’t draw anything. You can define paths without an available drawing context. To draw the path, you set a fill color on the current context (more on this below), and then fill the path.
Build and run the application, and you’ll see the green circle.
So far, you’ve discovered how easy it is to make custom-shaped views. You’ve done this by creating a UIButton subclass, overriding draw(_:) and adding the UIButton to your storyboard.
Behind the Scenes in Core Graphics
Each UIView has a graphics context, and all drawing for the view renders into this context before being transferred to the device’s hardware.
iOS updates the context by calling draw(_:) whenever the view needs to be updated. This happens when:
- The view is new to the screen.
- Other views on top of it are moved.
- The view’s
hiddenproperty is changed. - Your app explicitly calls the
setNeedsDisplay()orsetNeedsDisplayInRect()methods on the view.
Note: Any drawing done in draw(_:) goes into the view’s graphics context. Be aware that if you start drawing outside of draw(_:), as you’ll do in the final part of this tutorial, you’ll have to create your own graphics context.
You haven’t used Core Graphics yet in this tutorial because UIKit has wrappers around many of the Core Graphics functions. A UIBezierPath, for example, is a wrapper for a CGMutablePath, which is the lower-level Core Graphics API.
Note: Never call draw(_:) directly. If your view is not being updated, then call setNeedsDisplay() on the view.
setNeedsDisplay() does not itself call draw(_:), but it flags the view as ‘dirty’, triggering a redraw using draw(_:) on the next screen update cycle. Even if you call setNeedsDisplay() five times in the same method you’ll only ever actually call draw(_:) once.
@IBDesignable – Interactive Drawing
Creating code to draw a path and then running the app to see what it looks like can be about as exciting as watching paint dry, but you’ve got options. Live Rendering allows views to draw themselves more accurately in a storyboard, by running their draw(_:) methods. What’s more, the storyboard will immediately update to changes in draw(_:). All you need is a single attribute!
Still in PushButton.swift, just before the class declaration, add:
@IBDesignable
This is all that is needed to enable Live Rendering. Go back to Main.storyboard and notice that now, your button is shown as a green circle, just like when you build and run.
Now set up your screen so that you have the storyboard and the code side-by-side.
Do this by selecting PushButton.swift to show the code, then at the top right, click the Assistant Editor — the icon that looks like two intertwined rings. The storyboard should then show on the right-hand pane. If it doesn’t, you’ll have to choose the storyboard in the breadcrumb trail at the top of the pane:
Close the document outline at the left of the storyboard to free up some room. Do this either by dragging the edge of the document outline pane or clicking the button at the bottom of the storyboard:
When you’re all done, your screen should look like this:

In PushButton‘s draw(_:), change
UIColor.green.setFill()
to
UIColor.blue.setFill()
and you’ll (nearly) immediately see the change in the storyboard. Pretty cool!

Now you’ll create the lines for the plus sign.
Drawing Into the Context
Core Graphics uses a “painter’s model”. When you draw into a context, it’s almost like making a painting. You lay down a path and fill it, and then lay down another path on top and fill it. You can’t change the pixels that have been laid down, but you can “paint” over them.
This image from Apple’s documentation describes how this works. Just as it is when you’re painting on a canvas, the order in which you draw is critical.
Your plus sign is going on top of the blue circle, so first you code the blue circle and then the plus sign.
You could draw two rectangles for the plus sign, but it’s easier to draw a path and then stroke it with the desired thickness.
Add this struct and these constants inside of PushButton:
private struct Constants {
static let plusLineWidth: CGFloat = 3.0
static let plusButtonScale: CGFloat = 0.6
static let halfPointShift: CGFloat = 0.5
}
private var halfWidth: CGFloat {
return bounds.width / 2
}
private var halfHeight: CGFloat {
return bounds.height / 2
}
Now add this code at the end of the draw(_:) method to draw the horizontal dash of the plus sign:
//set up the width and height variables
//for the horizontal stroke
let plusWidth: CGFloat = min(bounds.width, bounds.height) * Constants.plusButtonScale
let halfPlusWidth = plusWidth / 2
//create the path
let plusPath = UIBezierPath()
//set the path's line width to the height of the stroke
plusPath.lineWidth = Constants.plusLineWidth
//move the initial point of the path
//to the start of the horizontal stroke
plusPath.move(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth - halfPlusWidth,
y: halfHeight))
//add a point to the path at the end of the stroke
plusPath.addLine(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth + halfPlusWidth,
y: halfHeight))
//set the stroke color
UIColor.white.setStroke()
//draw the stroke
plusPath.stroke()
In this block, you set up a UIBezierPath, give it a start position (left side of the circle) and draw to the end position (right side of the circle). Then you stroke the path outline in white. At this point, you should see this in the Storyboard:
In your storyboard, you’ll now have a blue circle with a dash in the middle of it:
That’s essentially what you do with the above code by using move(to:) and addLine(to:).
Now run the application on either an iPad 2 or an iPhone 6 Plus simulator, and you’ll notice the dash is not as crisp as it should be. It has a pale blue line encircling it.
Points and Pixels
Back in the days of the very first iPhones, points and pixels occupied the same space and were the same size, making them essentially the same thing. When retina iPhones came into existence, suddenly there were four times the pixels on the screen for the same number of points.
Similarly, the iPhone 6 Plus has once again increased the amount of pixels for the same points.
Note: The following is conceptual – the actual hardware pixels may differ. For example, after rendering 3x, the iPhone 6 Plus downsamples to display the full image on the screen. To learn more about iPhone 6 Plus downsampling, check out this great post.
Here’s a grid of 12×12 pixels, where points are shown in gray and white. The first (iPad 2) is a direct mapping of points to pixels. The second (iPhone 6) is a 2x retina screen, where there are 4 pixels to a point, and the third (iPhone 6 Plus) is a 3x retina screen, where there are 9 pixels to a point.
The line you’ve just drawn is 3 points high. Lines stroke from the center of the path, so 1.5 points will draw on either side of the center line of the path.
This picture shows drawing a 3-point line on each of the devices. You can see that the iPad 2 and the iPhone 6 Plus result in the line being drawn across half a pixel — which of course can’t be done. So, iOS anti-aliases the half-filled pixels with a color half way between the two colors, and the line looks fuzzy.
In reality, the iPhone 6 Plus has so many pixels, that you probably won’t notice the fuzziness, although you should check this for your own app on the device. But if you’re developing for non-retina screens like the iPad 2 or iPad mini, you should do anything you can to avoid anti-aliasing.
If you have oddly sized straight lines, you’ll need to position them at plus or minus 0.5 points to prevent anti-aliasing. If you look at the diagrams above, you’ll see that a half point on the iPad 2 will move the line up half a pixel, on the iPhone 6, up one whole pixel, and on the iPhone 6 Plus, up one and a half pixels.
In draw(_:), replace the move(to:) and addLine(to:) code lines with:
//move the initial point of the path
//to the start of the horizontal stroke
plusPath.move(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth - halfPlusWidth + Constants.halfPointShift,
y: halfHeight + Constants.halfPointShift))
//add a point to the path at the end of the stroke
plusPath.addLine(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth + halfPlusWidth + Constants.halfPointShift,
y: halfHeight + Constants.halfPointShift))
iOS will now render the lines sharply on all three devices because you’re now shifting the path by half a point.
Note: For pixel perfect lines, you can draw and fill a UIBezierPath(rect:) instead of a line, and use the view’s contentScaleFactor to calculate the width and height of the rectangle. Unlike strokes that draw outwards from the center of the path, fills only draw inside the path.
Add the vertical stroke of the plus just after the previous two lines of code, and before setting the stroke color in draw(_:). I bet you can figure out how to do this on your own, since you’ve already drawn a horizontal stroke:
You should now see the live rendering of the plus button in your storyboard. This completes the drawing for the plus button.
@IBInspectable – Custom Storyboard Properties
So you know that frantic moment when you tap a button more than needed, just to make sure it registers? Well, you need to provide a way for the user to reverse such overzealous tapping — you need a minus button.
A minus button is identical to the plus button except that it has no vertical bar and sports a different color. You’ll use the same PushButton class for the minus button, and declare what sort of button it is and its color when you add it to your storyboard.
@IBInspectable is an attribute you can add to a property that makes it readable by Interface Builder. This means that you will be able to configure the color for the button in your storyboard instead of in code.
At the top of the PushButton class, add these two properties:
@IBInspectable var fillColor: UIColor = UIColor.green
@IBInspectable var isAddButton: Bool = true
Change the fill color code at the top of draw(_:) from
UIColor.blue.setFill()
to:
fillColor.setFill()
The button will turn green in your storyboard view.
Surround the vertical line code in draw(_:) with an if statement:
//Vertical Line
if isAddButton {
//vertical line code move(to:) and addLine(to:)
}
//existing code
//set the stroke color
UIColor.white.setStroke()
plusPath.stroke()
This makes it so you only draw the vertical line if isAddButton is set – this way the button can be either a plus or a minus button.
The completed PushButton looks like this:
import UIKit
@IBDesignable
class PushButton: UIButton {
private struct Constants {
static let plusLineWidth: CGFloat = 3.0
static let plusButtonScale: CGFloat = 0.6
static let halfPointShift: CGFloat = 0.5
}
private var halfWidth: CGFloat {
return bounds.width / 2
}
private var halfHeight: CGFloat {
return bounds.height / 2
}
@IBInspectable var fillColor: UIColor = UIColor.green
@IBInspectable var isAddButton: Bool = true
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
let path = UIBezierPath(ovalIn: rect)
fillColor.setFill()
path.fill()
//set up the width and height variables
//for the horizontal stroke
let plusWidth: CGFloat = min(bounds.width, bounds.height) * Constants.plusButtonScale
let halfPlusWidth = plusWidth / 2
//create the path
let plusPath = UIBezierPath()
//set the path's line width to the height of the stroke
plusPath.lineWidth = Constants.plusLineWidth
//move the initial point of the path
//to the start of the horizontal stroke
plusPath.move(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth - halfPlusWidth + Constants.halfPointShift,
y: halfHeight + Constants.halfPointShift))
//add a point to the path at the end of the stroke
plusPath.addLine(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth + halfPlusWidth + Constants.halfPointShift,
y: halfHeight + Constants.halfPointShift))
if isAddButton {
//move the initial point of the path
//to the start of the horizontal stroke
plusPath.move(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth - halfPlusWidth + Constants.halfPointShift,
y: halfHeight + Constants.halfPointShift))
//add a point to the path at the end of the stroke
plusPath.addLine(to: CGPoint(
x: halfWidth + halfPlusWidth + Constants.halfPointShift,
y: halfHeight + Constants.halfPointShift))
}
//set the stroke color
UIColor.white.setStroke()
plusPath.stroke()
}
}
In your storyboard, select the push button view. The two properties you declared with @IBInspectable appear at the top of the Attributes Inspector:
Change Fill Color to RGB(87, 218, 213), and change the Is Add Button to off. Change the color by going to Fill Color\Other…\Color Sliders and entering the values in each input field next to the colors, so it looks like this:

The changes will take place immediately in the storyboard:
Pretty cool, eh? Now change Is Add Button back to on to return the button to a plus button.
A Second Button
Add a new UIButton to the storyboard and select it. Change its class to PushButton as you did it with previous one:

The green plus button will be drawn under your old plus button.
In the Attributes Inspector, change Fill Color to RGB(238, 77, 77) and change Is Add Button to off.
Remove the default title Button.
Add the Auto Layout constraints for the new view similarly to how you did before:
- With the button selected, Control-drag from the center of the button slightly to the left (still within the button), and choose Width from the popup menu.
- Similarly, with the button selected, Control-drag from the center of the button slightly up (still within the button), and choose Height from the popup menu.
- Control-drag left from inside the button to outside the button and choose Center Horizontally in Safe Area.
- Control-drag up from the bottom button to the top button, and choose Vertical Spacing.
After you add the constraints, edit their constant values in the Size Inspector to match these:
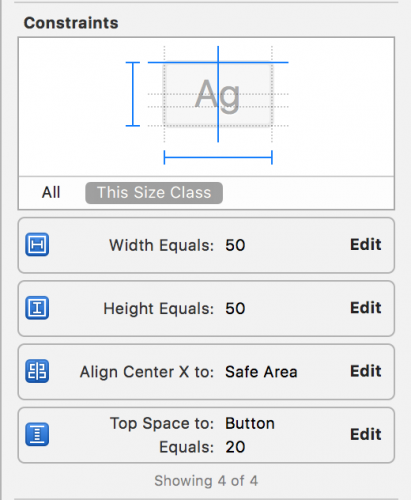
Build and run the application. You now have a reusable customizable view that you can add to any app. It’s also crisp and sharp on any size device. Here it is on the iPhone 4S.
Arcs with UIBezierPath
The next customized view you’ll create is this one:
This looks like a filled shape, but the arc is actually just a fat stroked path. The outlines are another stroked path consisting of two arcs.
Create a new file, File\New\File…, choose Cocoa Touch Class, and name the new class CounterView. Make it a subclass of UIView, and ensure the language is Swift. Click Next, and then click Create.
Replace the code with:
import UIKit
@IBDesignable class CounterView: UIView {
private struct Constants {
static let numberOfGlasses = 8
static let lineWidth: CGFloat = 5.0
static let arcWidth: CGFloat = 76
static var halfOfLineWidth: CGFloat {
return lineWidth / 2
}
}
@IBInspectable var counter: Int = 5
@IBInspectable var outlineColor: UIColor = UIColor.blue
@IBInspectable var counterColor: UIColor = UIColor.orange
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
}
}
Here you also create a struct with constants. Those constants will be used when drawing, the odd one out – numberOfGlasses – is the target number of glasses to drink per day. When this figure is reached, the counter will be at its maximum.
You also create three @IBInspectable properties that you can update in the storyboard. The variable counter keeps track of the number of glasses consumed, and it’s an @IBDesignable property as it is useful to have the ability to change it in the storyboard, especially for testing the counter view.
Go to Main.storyboard and add a UIView above the plus PushButton. Add the Auto Layout constraints for the new view similarly to how you did before:
- With the view selected, Control-drag from the center of the button slightly left (still within the view), and choose Width from the popup menu.
- Similarly, with the view selected, Control-drag from the center of the button slightly up (still within the view), and choose Height from the popup menu.
- Control-drag left from inside the view to outside the view and choose Center Horizontally in Safe Area.
- Control-drag down from the view to the top button, and choose Vertical Spacing.
Edit the constraint constants in the Size Inspector to look like this:

In the Identity Inspector, change the class of the UIView to CounterView. Any drawing that you code in draw(_:) will now show up in the view (but you’ve not added any yet!).
Impromptu Math Lesson
We interrupt this tutorial for a brief, and hopefully un-terrifying look back at high school level math. As Douglas Adams would say – Don’t Panic! :]
Drawing in the context is based on this unit circle. A unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1.0.
The red arrow shows where your arc will start and end, drawing in a clockwise direction. You’ll draw an arc from the position 3π / 4 radians — that’s the equivalent of 135º, clockwise to π / 4 radians – that’s 45º.
Radians are generally used in programming instead of degrees, and it’s useful to be able to think in radians so that you don’t have to convert to degrees every time you want to work with circles. Later on you’ll need to figure out the arc length, which is when radians will come into play.
An arc’s length in a unit circle (where the radius is 1.0) is the same as the angle’s measurement in radians. For example, looking at the diagram above, the length of the arc from 0º to 90º is π/2. To calculate the length of the arc in a real situation, take the unit circle arc length and multiply it by the actual radius.
To calculate the length of the red arrow above, you would simply need to calculate the number of radians it spans:
2π – end of arrow (3π/4) + point of arrow (π/4) = 3π/2
In degrees that would be:
360º – 135º + 45º = 270º

Back to Drawing Arcs
In CounterView.swift, add this code to draw(_:) to draw the arc:
// 1
let center = CGPoint(x: bounds.width / 2, y: bounds.height / 2)
// 2
let radius: CGFloat = max(bounds.width, bounds.height)
// 3
let startAngle: CGFloat = 3 * .pi / 4
let endAngle: CGFloat = .pi / 4
// 4
let path = UIBezierPath(arcCenter: center,
radius: radius/2 - Constants.arcWidth/2,
startAngle: startAngle,
endAngle: endAngle,
clockwise: true)
// 5
path.lineWidth = Constants.arcWidth
counterColor.setStroke()
path.stroke()
The following explains what each section does:
- Define the center point of the view where you’ll rotate the arc around.
- Calculate the radius based on the max dimension of the view.
- Define the start and end angles for the arc.
- Create a path based on the center point, radius, and angles you just defined.
- Set the line width and color before finally stroking the path.
Imagine drawing this with a compass — you’d put the point of the compass in the center, open the arm to the radius you need, load it with a thick pen and spin it to draw your arc.
In this code, center is the point of the compass, radius is the width that the compass is open (minus half the width of the pen) and the arc width is the width of the pen.
Note: When you’re drawing arcs, this is generally all you need to know, but if you want to dive further into drawing arcs, then Ray’s (older) Core Graphics Tutorial on Arcs and Paths will help.
In the storyboard and when you run your application, this is what you’ll see:
Outlining the Arc
When the user indicates they’ve enjoyed a glass of water, an outline on the counter shows the progress towards the goal of eight glasses.
This outline will consist of two arcs, one outer and one inner, and two lines connecting them.
In CounterView.swift , add this code to the end of draw(_:):
//Draw the outline
//1 - first calculate the difference between the two angles
//ensuring it is positive
let angleDifference: CGFloat = 2 * .pi - startAngle + endAngle
//then calculate the arc for each single glass
let arcLengthPerGlass = angleDifference / CGFloat(Constants.numberOfGlasses)
//then multiply out by the actual glasses drunk
let outlineEndAngle = arcLengthPerGlass * CGFloat(counter) + startAngle
//2 - draw the outer arc
let outlinePath = UIBezierPath(arcCenter: center,
radius: bounds.width/2 - Constants.halfOfLineWidth,
startAngle: startAngle,
endAngle: outlineEndAngle,
clockwise: true)
//3 - draw the inner arc
outlinePath.addArc(withCenter: center,
radius: bounds.width/2 - Constants.arcWidth + Constants.halfOfLineWidth,
startAngle: outlineEndAngle,
endAngle: startAngle,
clockwise: false)
//4 - close the path
outlinePath.close()
outlineColor.setStroke()
outlinePath.lineWidth = Constants.lineWidth
outlinePath.stroke()
A few things to go through here:
outlineEndAngleis the angle where the arc should end, calculated using the currentcountervalue.outlinePathis the outer arc. The radius is given toUIBezierPath()to calculate the actual length of the arc, as this arc is not a unit circle.- Adds an inner arc to the first arc. This has the same angles but draws in reverse (clockwise is set to false). Also, this draws a line between the inner and outer arc automatically.
- Closing the path automatically draws a line at the other end of the arc.
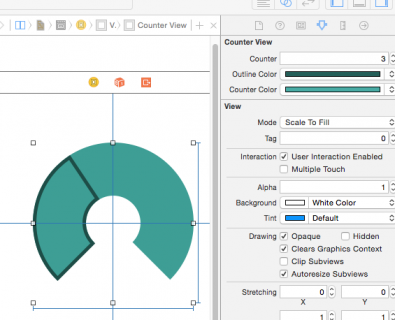
With the counter property in CounterView.swift set to 5, your CounterView should now look like this in the storyboard:
Open Main.storyboard, select the CounterView and in the Attributes Inspector, change the Counter property to check out your drawing code. You’ll find that it is completely interactive. Try adjusting the counter to be more than eight and less than zero. You’ll fix that up later on.
Change the Counter Color to RGB(87, 218, 213), and change the Outline Color to RGB(34, 110, 100).
Making it All Work
Congrats! You have the controls; all you have to do is wire them up so the plus button increments the counter and the minus button decrements the counter.
In Main.storyboard, drag a UILabel to the center of the Counter View, and make sure it is a subview of the Counter View. It will look like this in the document outline:
Add constraints to center the label both vertically and horizontally. In the end, the label should have constraints that look like this:

In the Attributes Inspector, change Alignment to center, font size to 36 and the default label title to 8.
Go to ViewController.swift and add these properties to the top of the class:
//Counter outlets
@IBOutlet weak var counterView: CounterView!
@IBOutlet weak var counterLabel: UILabel!
Still in ViewController.swift, add this method to the end of the class:
@IBAction func pushButtonPressed(_ button: PushButton) {
if button.isAddButton {
counterView.counter += 1
} else {
if counterView.counter > 0 {
counterView.counter -= 1
}
}
counterLabel.text = String(counterView.counter)
}
Here you increment or decrement the counter depending on the button’s isAddButton property, make sure the counter doesn’t drop below zero — nobody can drink negative water. :] You also update the counter value in the label.
Also add this code to the end of viewDidLoad() to ensure that the initial value of the counterLabel will be updated:
counterLabel.text = String(counterView.counter)
In Main.storyboard, connect the CounterView outlet and UILabel outlet. Connect the method to the Touch Up Inside event of the two PushButtons.
Run the application and see if your buttons update the counter label. They should.
But wait, why isn’t the counter view updating?
Think way back to the beginning of this tutorial, and how you only call draw(_:) when other views on top of it are moved, or its hidden property is changed, or the view is new to the screen, or your app calls the setNeedsDisplay() or setNeedsDisplayInRect() methods on the view.
However, the Counter View needs to be updated whenever the counter property is updated, otherwise the user will think your app is busted.
Go to CounterView.swift and change the counter property declaration to:
@IBInspectable var counter: Int = 5 {
didSet {
if counter <= Constants.numberOfGlasses {
//the view needs to be refreshed
setNeedsDisplay()
}
}
}
This code makes it so that the view refreshes only when the counter is less than or equal to the user's targeted glasses, as the outline only goes up to 8.
Run your app again. Everything should now be working properly.
Where to Go From Here?
You've covered basic drawing in this tutorial, and you should now be able to change the shape of views in your UIs. But wait - there’s more! In Part 2 of this tutorial , you’ll explore Core Graphics contexts in more depth and create a graph of your water consumption over time.
You can download the project with all the code up to this point.
If you have any questions or comments please join the forum discussion below.
The post Core Graphics Tutorial Part 1: Getting Started appeared first on Ray Wenderlich.