Update Note: This Beginning Android Development tutorial is now up to date with the latest version of Android Studio, version 3.0, and uses Kotlin for app development. Update by Joe Howard. Original tutorial by Matt Luedke. Previous updates by Megha Bambra and Brian Voong.

Android Studio is an IntelliJ IDEA based IDE and is the official IDE for Android application development.
In this Android Studio tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the tools that every Android developer uses to create a simple fortune-telling app. You’ll learn to use some of Android Studio’s key features such as:
- Navigating through different files in your project using the project explorer
- Working with the AndroidManifest.xml file
- Learning about the Gradle build system
- Importing files into your project
- Learning about the rich layout editor with dynamic layout previews
- Using Logcat and the Android Monitor to debug your app
Note: This tutorial assumes that you’ve already installed Android Studio 3.0 or later and have set up an emulator or a device configured for testing. If you haven’t, please refer to our previous tutorial about installing Android Studio to get up and running in no time!
Getting Started with Android Studio
You’ll start by creating a brand new Android app that you’ll use to explore Android Studio and learn about its capabilities and interface.
For bonus points, you’ll also walk away as a bonafide fortune teller — or something to that effect. At least you’ll have a fun app to play around with!
Fire up Android Studio and in the Welcome to Android Studio window, select Start a new Android Studio project.
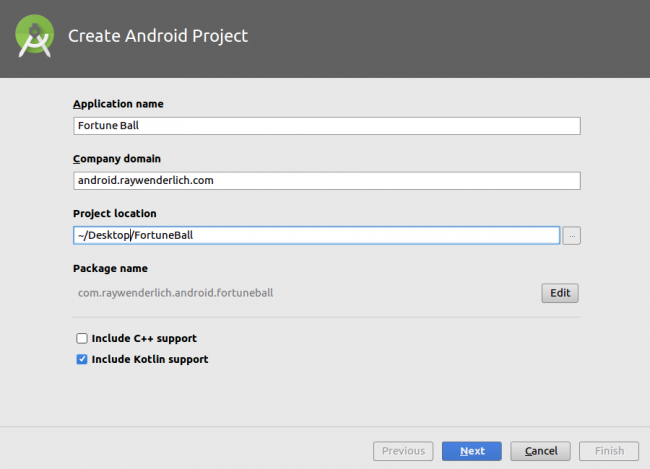
In the Create Android Project window, set the Application name as Fortune Ball, enter a Company domain of your choosing, and select a convenient location to host your application in the Project location field. Also, make sure that Include Kotlin supportClick Next.
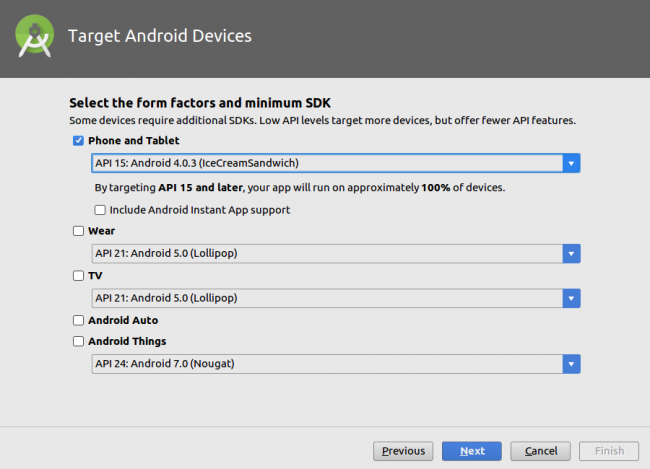
Now you’re looking at the Target Android Devices window. Check the Phone and Tablet box and specify API 15 as the Minimum SDK. Click Next.
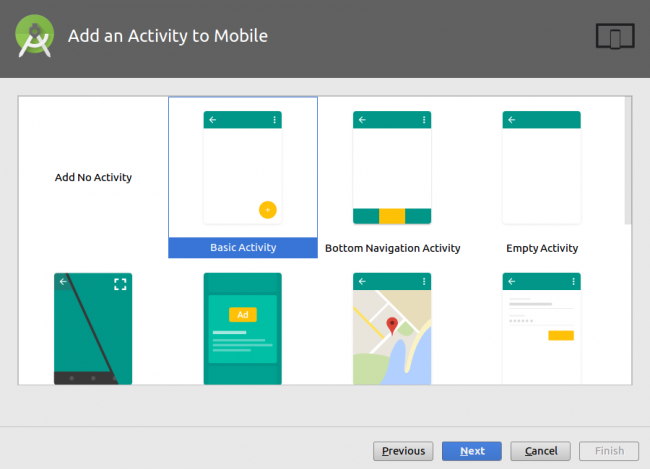
From the Add an Activity to Mobile window, select Basic Activity. Take a half minute here to look at all your options; this window gives you an overview of the layout template. In this case, it’ll be a blank activity with a toolbar at the top and a floating action button at the bottom. Click Next to proceed.
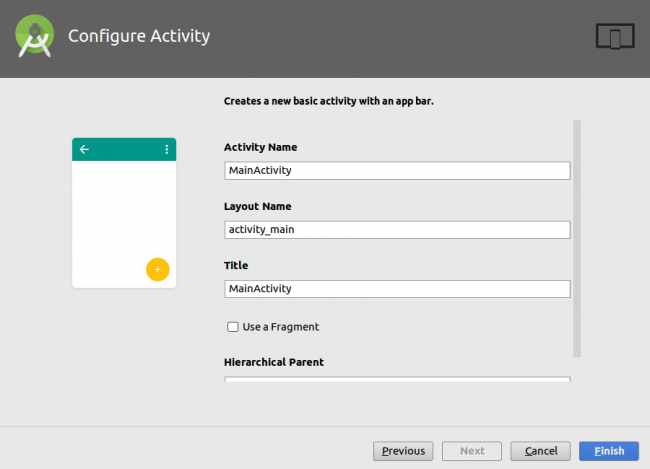
In the Configure Activity window, which is shown in the screenshot below, you’ll have the option to change Activity Name, Layout Name, Title and Hierarchical Parent. For the purposes of this tutorial, keep it simple and accept the default values by clicking Finish.
Within a short amount of time (hopefully seconds!), you’ll land on a screen that looks similar to this:
Build and run your application and you should see a similar screen on your device or emulator. Note that the emulator acts like a device, so it will need time to boot and load.
Voila. That’s an app! There’s not much to it, but it’s enough to dive into the next section.
Project and File Structure
For this portion of the tutorial, your focus will be on the highlighted section of the screenshot below. This window shows the project files of your application. By default, the files are filtered to show Android project files.
When you select the file dropdown menu as illustrated in the screenshot below, you’ll see several options to filter the files. The key filters here are Project and Android.
The Project filter will show you all the application modules — there is a minimum of one application module in every project.
Other types of modules include third-party library modules or other Android application modules (such as Android wear apps, Android TV, etc…). Each module has its own complete source sets, including a gradle file, resources and source files, e.g. Kotlin files.
Note: If you don’t see the project view open, you can click on the Project tab on the left side panel as indicated in the screenshot above.
The default filter is Android which groups files by specific types. You’ll see the following folders at the very top level:
Note that the source folder is named java even if you’re using Kotlin. You’ll take a deeper dive into each of these folders, starting with manifests, in the next section.
Overview of AndroidManifest.xml
Every Android application contains the AndroidManifest.xml file found in the manifests folder. This XML file informs your system of the app’s requirements and must be present in order for the Android system to build your app.
Go to the app’s manifests folder and expand to select AndroidManifest.xml. Double click on the file to open.
The manifest and application tags are required in the manifest file and must only appear once.
In addition to the element name, each tag also defines a set of attributes. For example, some of the many attributes in the application tag are: android:icon, android:label and android:theme.
Other common elements that can appear in the manifest include:
uses-permission: requests a special permission that must be granted to the application in order for it to operate correctly. For example, an app must request permission from the user in order to access the Internet—in this case you must specify the android.permission.INTERNET permission.activity: declares an activity that implements part of the application’s visual user interface and logic. Every activity that your app uses must appear in the manifest—undeclared activities won’t be seen by the system and sadly, they’ll never run.service: declares a service that you’re going to use to implement long-running background operations or a rich communications API that can be called by other applications. An example includes a network call to fetch data for your application. Unlike activities, services have no user interface.receiver: declares a broadcast receiver that enables applications to receive intents broadcast by the system or by other applications, even when other components of the application are not running. One example of a broadcast receiver would be when the battery is low and you get a system notification within your app, allowing you to write logic to respond.You can find a full list of tags allowed in the manifest file here on the Android Developer site.
Configuring the Manifest
You’re currently looking at an excellent example of a framework, but a terrible fortune teller; you’re here because you want to learn how to play around on Android. That’s rather convenient because the manifest needs some changes so you can look into the future.
Under the activity tag for MainActivity, add the attribute android:screenOrientation="portrait" to restrict the screen to portrait mode only. If it’s absent, the screen will transform to landscape or portrait mode depending on the device’s orientation. After adding this attribute, your manifest file should look like the screenshot below:
Build and run the app. Rotate your phone or emulator. Notice that the screen doesn’t transform into landscape mode as you have restricted this capability in the manifest file.
Overview of Gradle
Let’s shift gears to Gradle. In a nutshell, it’s a build system that’s utilized by Android Studio. It takes the Android project and builds/compiles it into an installable Android Package Kit (APK) file that in turn can be installed on devices.
As shown below, you can find the build.gradle file, located under Gradle scripts, in your project at two levels: module level and project level. Most of the time, you’ll edit the module level file.
Open up the build.gradle (Module:app) file. You’ll see the default gradle setup:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'kotlin-android'
apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions'
android {
compileSdkVersion 26
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.raywenderlich.android.fortuneball"
minSdkVersion 15
targetSdkVersion 26
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jre7:$kotlin_version"
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
implementation 'com.android.support:design:26.1.0'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.1'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.1'
}
Let’s step through the major components:
-
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'applies the Android plugin at the parent level and makes available the top level build tasks required to build an Android app. -
apply plugin: 'kotlin-android'andapply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions'apply Kotlin related plugins that allow your app to use the Kotlin compiler and Android-specific Kotlin extensions - Next in the
android{...}section, you get configuration options such astargetSdkVersion. The target SDK for your application should be kept at the latest API level (26 as we publish this tutorial). Another important component is theminSDKVersionwhich defines the minimum SDK version a device should have installed in order to run your application. For example, if your device’s SDK version was 14, then this app won’t be able to run on that device since here the minimum supported version is 15. - The last component is
dependencies{...}. Important dependencies to note areimplementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:VERSION'andimplementation 'com.android.support:design:VERSION'. They provide support and compatibility with the new features from the latest API to the older APIs. - The dependency
implementation"org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jre7:$kotlin_version"allows your code to use the Kotlin standard library.
In addition to Android compatibility libraries, you can also add other third party libraries in the dependencies{...} component. You’ll add an animation library where you’ll be able to add some cool effects to user interface elements in your application. Find dependencies, and add the following two lines at the bottom:
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.daimajia.easing:library:2.0@aar'
implementation 'com.daimajia.androidanimations:library:2.2@aar'
}
Here you added two new third-party dependencies that will help you make FortuneBall shine. These libraries will be automatically downloaded and integrated by Android Studio.
In fact, once you add these dependencies, Android Studio realizes that it needs to download them and tells you as much. Look for a bar across the top of the build.gradle file as shown the next screenshot. Click Sync Now to integrate these dependencies in your app.
Syncing takes couple of seconds. You can monitor the Gradle file update in the Messages tab in the bottom panel. Look for a success message in that panel as shown in the screenshot below.
Alright, that’s all the config you need to do to Gradle for now. The whole point of this was so that you’re setup to add some fancy animations to your application, which you’ll do in a bit.
Importing files
An important part of making an Android app involves integrating other resources such as images, custom fonts, sounds, videos etc. These resources have to be imported into Android Studio and must be placed in appropriate folders. This allows the Android operating system to pick the correct resource for your app.
For Fortune Ball, you’ll be importing image assets and will place them in drawable folders. Drawable folders can hold images or custom XML drawables (i.e. you can draw shapes via XML code and use them in your app’s layouts).
To get started, download the image assets here, then unzip the contents and save them where they can be easily accessed.
Back in the project in Android Studio, switch the view from Android to Project. Open the res folder under app > src > main. Right click on the res folder, select New > Android resource directory.
You’ll get a window titled New Resource Directory. From the Resource type dropdown select the drawable option. In the Available qualifiers list, select Density and click the button highlighted in the screenshot below:
In the subsequent window, select XX-High Density from the Density dropdown. Click OK.
Repeat the same process and create drawable-xhdpi, drawable-hdpi and drawable-mdpi folders by selecting X-High Density, High Density, and Medium Density, respectively, from the Density dropdown.
Each drawable folder that has a density qualifier (i.e. xxhdpi, xhdpi, hdpi) houses images corresponding to that particular density or resolution. For example, the folder drawable-xhdpi contains images that are extra-high density, meaning an Android device with an extra-high resolution screen will pick images from this folder. This allows your app to look great on all Android devices, irrespective of the screen quality. To learn more about screen densities, check out the Android documentation.
After creating all the drawable folders, go back to the unzipped contents in your file manager, and copy (cmd + C on Mac, Ctrl+C on PC) the image file img_crystral.png from each folder and paste (cmd + V, Ctrl+V on PC) it into the corresponding folder in Android Studio.
When you paste the files, you’ll be presented with the Copy window. Select OK.

You’ve just put the ball in Fortune Ball and know how to import things now. Looks like you just checked another feature off your to-learn list!
XML View with Dynamic Layout Previews
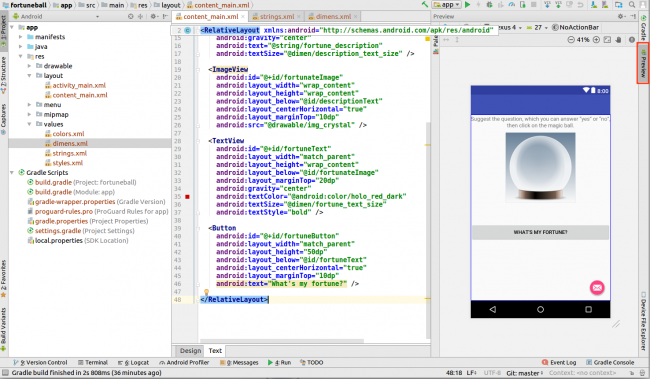
An incredibly important part of building an Android application is creating a layout that the users of the application interact with. In Android Studio, you do this task in the layout editor. Open up content_main.xml from res/layout. You’ll initially land on the Design tab of the layout editor. In this tab, you can drag user interface elements like buttons, text fields etc. in the editor.
On the right hand side of the Design tab is the Text tab. Switching to this view allows you to edit the XML that makes up the layout directly.
In both tabs, you’ll be able to preview the layout in the device as you build. Choose the Text tab to start building the layout for Fortune Ball.
Before you start building the view, you need to define some values. Open up strings.xml under res/values and add the following:
<string name="fortune_description">Suggest the question, which you can answer “yes” or “no”, then click on the magic ball.</string>
strings.xml contains all the user-facing strings that appear in your app. Splitting the strings out into their own file makes internationalization a breeze, as you just provide a strings file for each language you wish to support. Although you might not want to translate your app right away, it’s considered a best-practice to use a strings file.
Next, open dimens.xml under res/values and add the following:
<dimen name="description_text_size">15sp</dimen>
<dimen name="fortune_text_size">20sp</dimen>
dimens.xml contains all the dimensions values such as margin spacing for your layouts, sizes of text etc. Again, it’s a good practice to keep the dimensions in this file so that they can be re-used in constructing layouts.
Head back to content_main.xml and replace the entire contents of the file with the code below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
tools:showIn="@layout/activity_main">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/descriptionText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/fortune_description"
android:textSize="@dimen/description_text_size" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/fortunateImage"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/descriptionText"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:src="@drawable/img_crystal" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/fortuneText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/fortunateImage"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColor="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
android:textSize="@dimen/fortune_text_size"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/fortuneButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_below="@id/fortuneText"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="What's my fortune?" />
</RelativeLayout>
This rather large chunk of XML creates the layout of FortuneBall. At the top level you’ve added a RelativeLayout, whose job it is to layout its contents. It is stretched to match the size of its parent (i.e. the full activity).
Within the relative layout you added two pieces of text, an image and a button. These will appear within the container in the order that you added them, and their content is read from the strings.xml in the case of the text views, and from the drawable you added in the case of the image.
As you’re updating content_main.xml, notice how the Preview window updates the UI:
Note: If you can’t see the preview window, then click on the Preview button on the right-hand side panel of the layout editor while you’re still in the Text tab.
Build and run.
Congrats! You’ve designed your app’s layout. However, it’s only a pretty picture at this point — clicking on that button doesn’t do anything. Ready to play around with activities?
Connecting Views with Activities
You use the java files located in app / src / main / java to implement your app’s logic.
Open MainActivity.kt and add these imports directly below the existing imports
import java.util.Random
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.ImageView
import android.widget.TextView
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
import com.daimajia.androidanimations.library.Techniques
import com.daimajia.androidanimations.library.YoYo
The first six imports indicate that you will be referencing the Random, View, Button, ImageView, TextView, and Toolbar classes in your code. The next two imports indicate that you will be using two classes from the libraries included in the build.gradle earlier for animations. Inside of MainActivity.kt add the following at the top of the MainActivity class:
private var fortuneList = arrayOf("Don’t count on it", "Ask again later", "You may rely on it", "Without a doubt", "Outlook not so good", "It's decidedly so", "Signs point to yes", "Yes definitely", "Yes", "My sources say NO")
private lateinit var fortuneText: TextView
private lateinit var generateFortuneButton: Button
private lateinit var fortuneBallImage: ImageView
In this small chunk of code you’ve declared 4 member variables for the activity. The first is an array of strings that represent the possible fortunes, and the remaining three represent the UI elements you created in the layout.
Next, replace the content of the onCreate() method with the following:
// 1:
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 2:
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val toolbar = findViewById<View>(R.id.toolbar) as Toolbar
setSupportActionBar(toolbar)
// 3:
fortuneText = findViewById<View>(R.id.fortuneText) as TextView
fortuneBallImage = findViewById<View>(R.id.fortunateImage) as ImageView
generateFortuneButton = findViewById<View>(R.id.fortuneButton) as Button
// 4:
generateFortuneButton.setOnClickListener {
// 5:
val index = Random().nextInt(fortuneList.size)
fortuneText.setText(fortuneList[index])
// 6:
YoYo.with(Techniques.Swing)
.duration(500)
.playOn(fortuneBallImage)
}
Taking the numbered sections one-by-one:
- Call the superclass implementation to ensure the activity is ready to go.
- Specify that the layout for this activity is provided by the layout you created before, and perform some preparation on the toolbar.
- Populate the values of the three member variables you created before for the views in the layout using the
findViewByIdmethod. Theidvalue is the same as the one you provided in the XML layout. (Note: since you are using Kotlin Android Extensions, you don’t really need thefindViewByIdcalls; see more here.) - Add an
OnClickListenerto the button. This is a simple class that encapsulates the functionality you’d like to perform when the button is pressed. - Find a random fortune from the
fortuneListarray, and update the fortune text to show it. - Use the third-party animation library you added as a dependency to the gradle file to add a fun animation to the crystal ball image.
OK—that wasn’t too bad right? Build and run, and hit the button to test out your fortune-telling powers.
Tidy Up
You’re almost done. But before you start planning your release party, you have some clean up ahead, like getting rid of that floating button. Head to res / layout and open activity_main.xml.
This layout file contains a reference to content_main.xml that you previously edited. It wraps the content with the default toolbar and floating action button. However, Fortune Ball doesn’t need a floating action button, so remove the following code block from this xml file:
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|end"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/fab_margin"
app:srcCompat="@android:drawable/ic_dialog_email" />
Build and run. You won’t be seeing that the floating button on the bottom right-hand corner around here anymore:
Ask a question, click or tap on What’s my fortune? and let your future unfold before your eyes!
Logcat
Android Studio provides a bunch of tools to help you look under the hood of your application. They can be accessed from the View / Tool Windows menu, or by clicking the tabs at the bottom of Android Studio:
Let’s walk through one of them. Don’t worry; you don’t have to memorize all this and there won’t be a quiz. :]
Click the Logcat tab:
At the top you specify the device or emulator you want to monitor, and the “process” you are most interested in (you should select your app’s package name if it’s not already selected).
The Logcat tab has camera and play buttons to enable taking screenshots or screen video recordings, respectively.
Logcat gives you a detailed view into your device’s system messages with the ability to drill down into a specific application, or even use the search bar to filter out messages unless they contain specific text.
Make sure you’ve selected Show only selected application in the top right, as shown in the screenshot earlier. Now, you will only see messages from your app, including those you write yourself. Oh, what? You’ve not added any messages for yourself?
Head to MainActivity.kt and add the following to the list of imports
import android.util.Log
At the end of onCreate() in MainActivity add the following line:
Log.v("FORTUNE APP TAG","onCreateCalled")
The Log.v calls for two parameters — a tag and a message. In this case, you’ve defined the tag as "FORTUNE APP TAG" and the message as "onCreateCalled".
Build and run the app so you can see this log message in the Logcat panel.
To filter the LogCat contents to just your message alone, type onCreateCalled into the search box above the console, like this:
Then remove your search text to see all the log messages again.
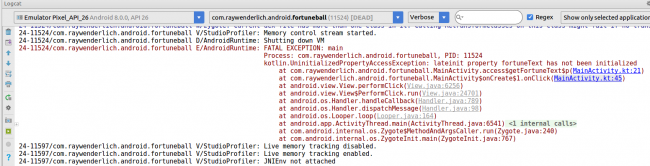
Another very useful utility of logcat is the ability to see stacktrace or error messages from app crashes and exceptions. You’ll add a bug to your perfectly working app to see how that works.
Go to MainActivity.kt and comment out the following line in onCreate():
//fortuneText = findViewById<View>(R.id.fortuneText) as TextView
Build and run the application. Once it launches click the What’s My Fortune? button on the screen. Oh no! It crashed.

How would you go about fixing this if you hadn’t put the bug in on purpose? Logcat to the rescue!
Head back to the Logcat panel — it’ll look something like this:
That sure is a lot of red text, and it’s exactly where to go sniffing around for clues. You’re looking for an exception somewhere. In this case, it’s line 45 in the MainActivity.kt file. LogCat has even helpfully turned that link into a blue hyperlink, and if you click it you will be taken right to the problematic line!
By commenting out fortuneText = findViewById, you created a variable but didn’t assign it a value — hence the uninitialized property access exception.
Go ahead and uncomment that code and build and run the application. This time there’s no crash!
Logcat is a powerful tool that lets you debug your application errors and exceptions.
Where to Go From Here?
You can download the final project here.
Practice makes perfect! You’ve learned your way around and can now create a project, play around with Gradle, import assets, set up layouts and do some testing.
There’s a lot of cool stuff to learn about Android, and I suggest you start with these next steps:
- Get familiar with Logcat and the filtering mechanism. Filter by different criteria.
- There will be times where you’ll want to test your application’s robustness in different network environments. See the Android Emulator 2.0 section of our Android Studio 2 tour for more details.
- This beginning Android development tutorial has just touched on some of the tools used to build out the layout and UI. To learn more, pour over the official Android documentation for UI.
- Keep coming back to raywenderlich.com—- we’ve got some great Android content coming your way over the next days, weeks and months.
- Talk to other developers. Make use of the forums below and ask your questions, share your findings and pick up tips.
This is it folks! Give yourself a round of applause and stay tuned for more awesome tutorials from your Android team. :]
The post Beginning Android Development with Kotlin, Part Two: Using Android Studio appeared first on Ray Wenderlich.